Understanding the Average U.s. Family Income is crucial for grasping the economic well-being of households across the nation. While numerous factors contribute to the financial landscape of American families, examining specific sectors like farm households offers valuable insights. Recent data from the U.S. Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service (ERS) sheds light on the income dynamics within farm households, providing a detailed snapshot of their financial status and contributing to a broader understanding of average U.S. family income trends.
Median vs. Average Income: Why Median Matters
When discussing income, it’s important to distinguish between average (mean) and median figures. The median income represents the midpoint – half of households earn more, and half earn less. Economists often prefer median income as it is less skewed by extremely high or low incomes, providing a more representative measure of the typical household’s financial situation. Therefore, when we analyze “average U.S. family income,” focusing on the median offers a more accurate picture of the financial experiences of most families.
2023 U.S. Farm Household Income: A Detailed Look
In 2023, the estimated median total income for U.S. farm households experienced a decrease compared to 2022. This decline was observed across median farm income and median off-farm income as well. Specifically, the median household income from farming was -$900, indicating that at the midpoint, farm operations, on average, did not generate profit for farm households in 2023. This highlights a key characteristic of the U.S. agricultural landscape: many farms, particularly smaller ones, struggle to be profitable from farming alone, even in favorable economic periods.
Despite the negative median farm income, off-farm income played a crucial role in the financial stability of farm households. The median off-farm income reached $79,900 in 2023. When combined with farm income, the median total household income for farm families stood at $97,984. It’s important to note that due to the varied distribution of farm and off-farm income, the median total income is not simply the sum of the median off-farm and median farm income.
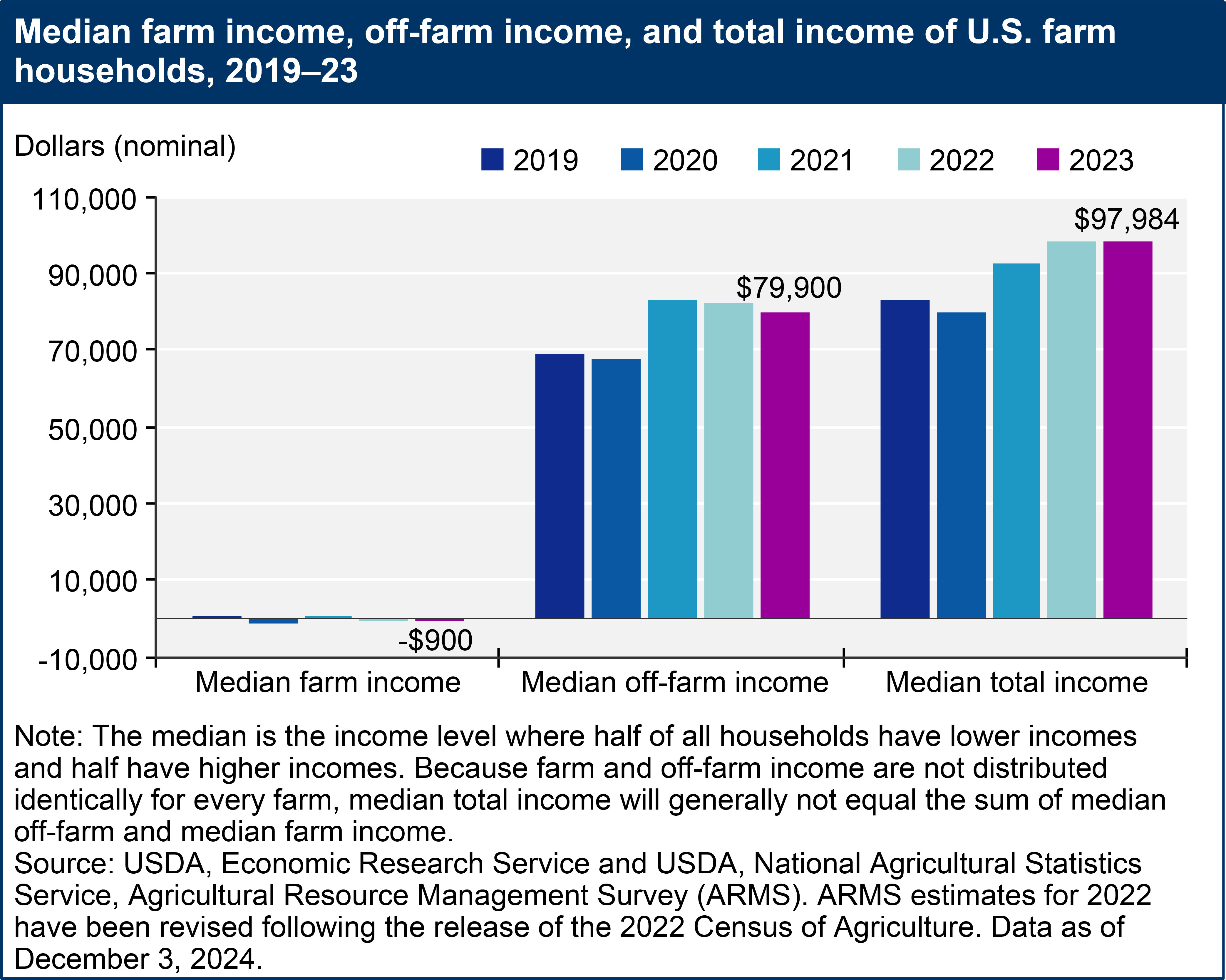 A bar chart shows the median farm income, off-farm income, and total income of U.S. farm households for the years 2019 through 2023.
A bar chart shows the median farm income, off-farm income, and total income of U.S. farm households for the years 2019 through 2023.
Income Variation by Farm Type
The USDA, ERS categorizes farms into different types based on their annual gross cash farm income and the principal operator’s occupation. This typology reveals significant variations in income levels. Small family farms, with less than $350,000 in annual gross cash farm income, are further classified as residence farms (operator’s primary occupation is not farming or they are retired) or intermediate farms (farming is the primary occupation). Commercial farms, on the other hand, have a gross cash farm income of $350,000 or more.
In 2023, commercial family farms demonstrated a significantly higher median farm income of $167,550 and a median total household income of $253,496. In contrast, intermediate farms reported a median farm income of -$1,974 and a median total household income of $62,014. Residence farms, despite having a similar median farm income of -$1,980, achieved a higher median total income of $116,493 due to substantial off-farm income. These figures underscore that the average U.S. family income within the farm sector is heavily influenced by the scale of farming operations and the reliance on off-farm income sources.
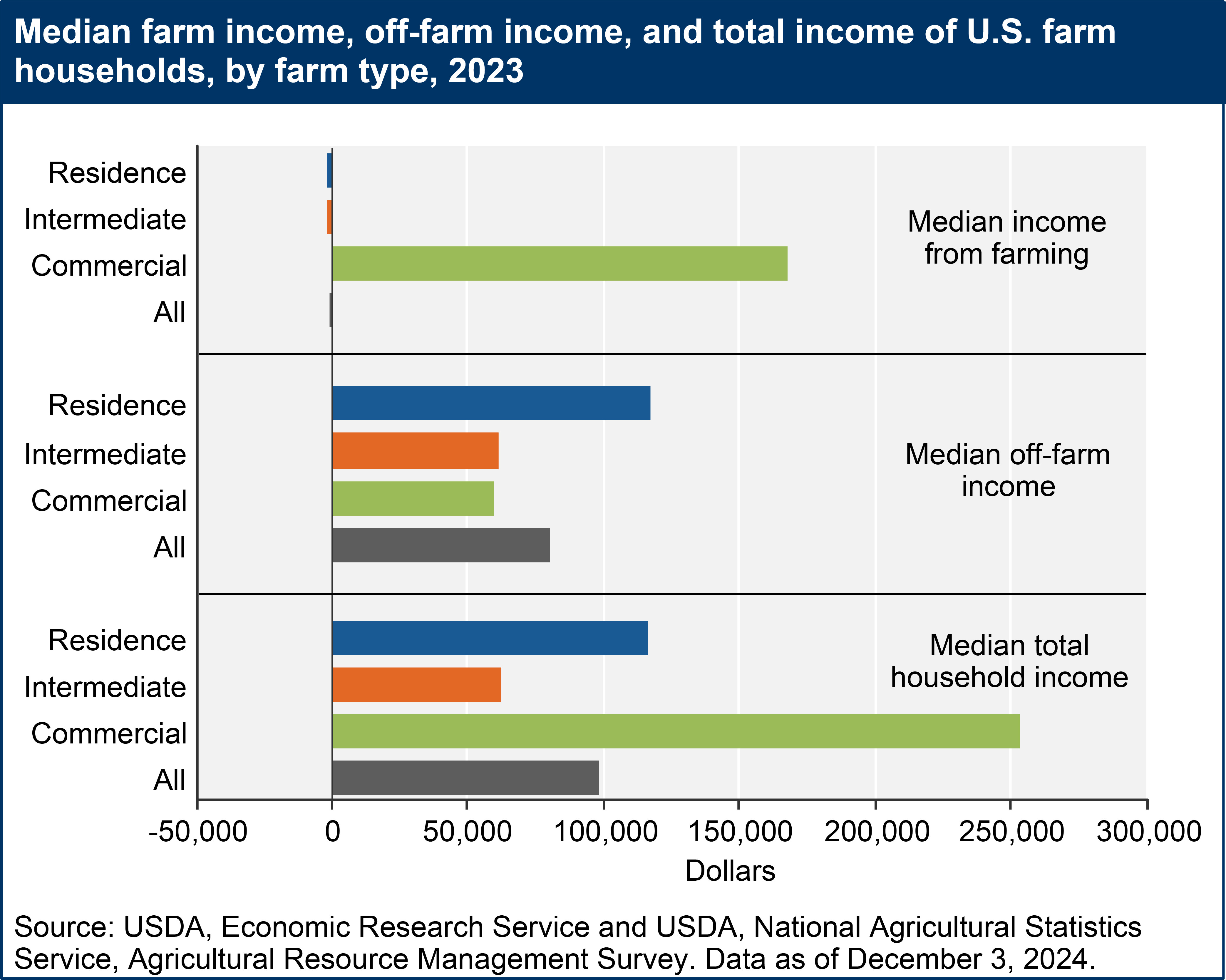 A bar chart shows the median farm income, off-farm income, and total income of U.S. farm households, by farm type in 2023
A bar chart shows the median farm income, off-farm income, and total income of U.S. farm households, by farm type in 2023
The Significant Role of Off-Farm Income
The data clearly highlights the critical role of off-farm income in the financial well-being of many U.S. farm families. For residence and intermediate farms, off-farm income often compensates for lower or even negative farm income, contributing significantly to their total household income and bringing their total income closer to the average U.S. family income. This reliance on off-farm income is a notable trend in the agricultural sector, reflecting the diversification strategies employed by farm households to ensure financial stability.
Looking at the share of households with positive farm income further illustrates this point. In 2023, only 39 percent of residence farms and 46 percent of intermediate farms had positive income from farming. However, for those with positive farm income, it constituted a small share of their total household income – 6 percent for residence farms and 27 percent for intermediate farms at the median. Conversely, commercial farms are much more reliant on farm income, with 84 percent having positive farm income, contributing to 80 percent of their total household income at the median.
 A bar chart shows the percent of U.S. farm households with positive farm income and their median share of total household income from farming in 2023
A bar chart shows the percent of U.S. farm households with positive farm income and their median share of total household income from farming in 2023
Impact of Commodity Specialization and Regional Factors
Farm household income is also influenced by commodity specialization and geographic location. Farms specializing in different commodities experience varying market conditions and production demands, impacting their profitability and, consequently, household income. For instance, dairy farms often require extensive and consistent labor, potentially limiting off-farm employment opportunities for operators.
Furthermore, income levels vary across different Farm Resource Regions in the U.S., reflecting regional differences in farm types, commodity specialization, and agro-climatic conditions. In 2023, the Northern Great Plains and Heartland regions stood out with consistently positive median farm incomes and the highest total household incomes. These regions, characterized by cash grain and cattle farms in the Heartland and wheat and barley production in the Northern Great Plains, demonstrate the impact of regional agricultural strengths on farm household financial well-being.
 A bar chart shows 2 bars, one for median farm income and and one for median total income of U.S. farm households by commodity specialization in 2023
A bar chart shows 2 bars, one for median farm income and and one for median total income of U.S. farm households by commodity specialization in 2023
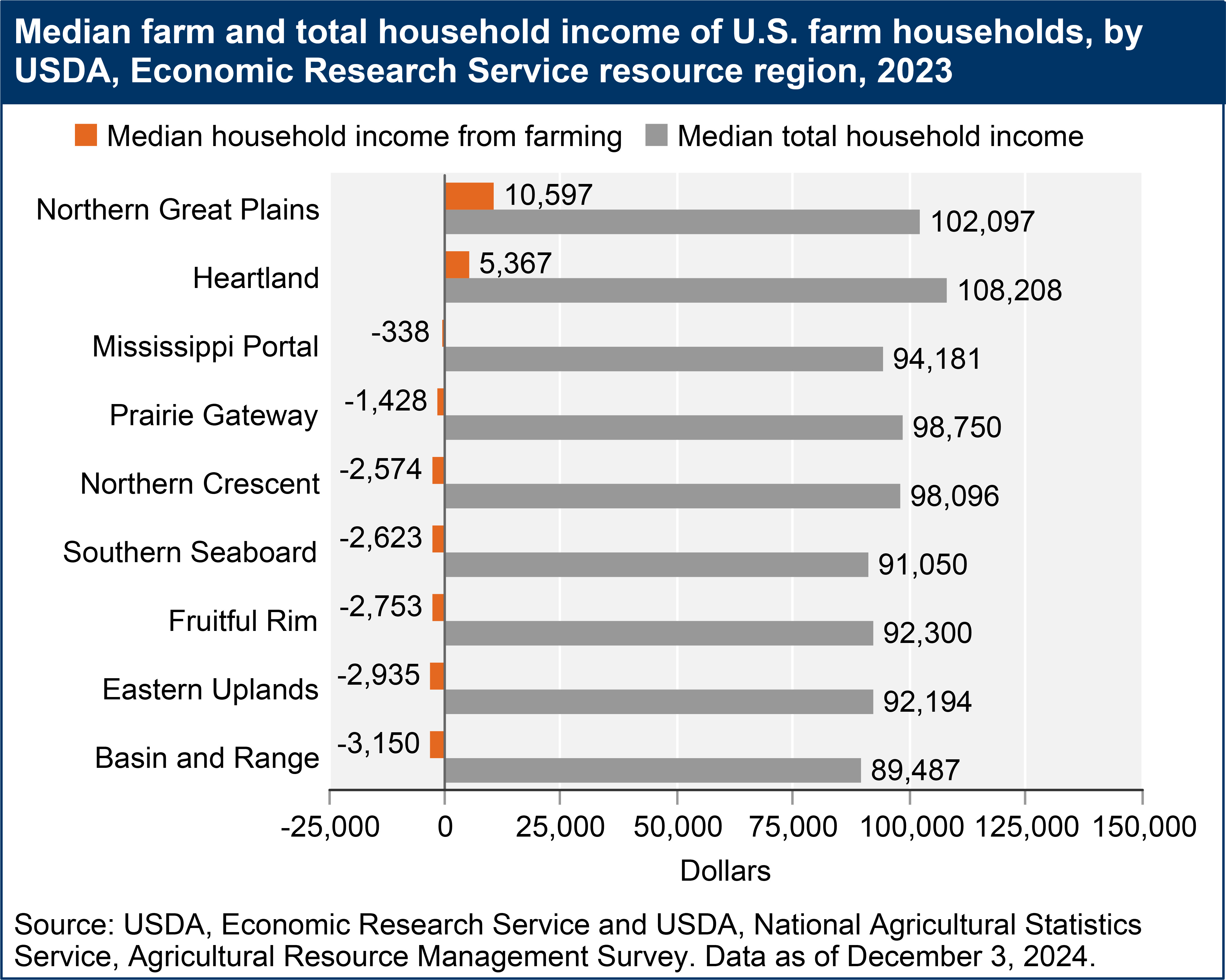 A bar chart shows the median farm and total household income of U.S. farm households, by USDA, Economic Research Service resource region in 2023
A bar chart shows the median farm and total household income of U.S. farm households, by USDA, Economic Research Service resource region in 2023
Conclusion
Analyzing farm household income provides a valuable lens through which to understand the complexities of average U.S. family income. The data reveals significant variations based on farm type, commodity specialization, regional location, and the crucial role of off-farm income. While median farm household income experienced a decrease in 2023, off-farm income continues to be a vital component, particularly for smaller and residence farms, influencing their overall financial health and contributing to the diverse landscape of average U.S. family income. These insights underscore the importance of considering various factors when assessing the economic well-being of American families and the agricultural sector’s place within the broader economy.
